How proficient is your English? What kinds of tasks can you use it for? A proficiency test will help employers and schools to understand your language skills level. What do the different tests offer and how to compare across them?
Here we take a closer look at the ACTFL proficiency test. We’ll discuss:
- What is ACTFL and what does it measure?
- Which test is more difficult;
- Reasons for taking each test.
- ACTFL scores equivalency tables in case you wish to take the TOEFL or in case you wish to take the IELTS.
All set? Here we go!
What Is the ACTFL and what does it aim to achieve?
There are many language proficiency levels in English and many ways to evaluate them, such as the ILR, the CEFR language scale, and so on. We’ll be looking at one of them – the ACTFL.
First things first. Before ACTFL there was the ILR – Interagency Language Roundtable.
The ILR was officially created in 1973, although it has been around informally since the 50’s. It was originally conceived so that the US government and federal agencies could share and improve their techniques and technology for language learning, and language testing.
The ILR created a scale with 5 proficiency levels, ranging from 0 to 5, where 0 equates to no knowledge of a language, and 5 equates a native speaker or highly proficient non-native speaker.
The ILR scale still exists, but gave rise to ACTFL and its proficiency guidelines and ACTFL scale. Where the ILR scale uses a simple ‘+’, the ACTFL proficiency scale employs sub-levels to pinpoint a person’s language proficiency.
ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines & Scales Explained
The ACTFL scale has 5 main levels – Novice, Intermediate, Advanced, Superior – which are divided into 3 sub-levels (Low, Mid, and High), plus Distinguished. The ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines describe what individuals can do with language in: speaking, writing, listening, and reading.
The goal of the ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines is to give an individual’s level in real-world situations – spontaneous and non-rehearsed.
The ACTFL Proficiency Scale :
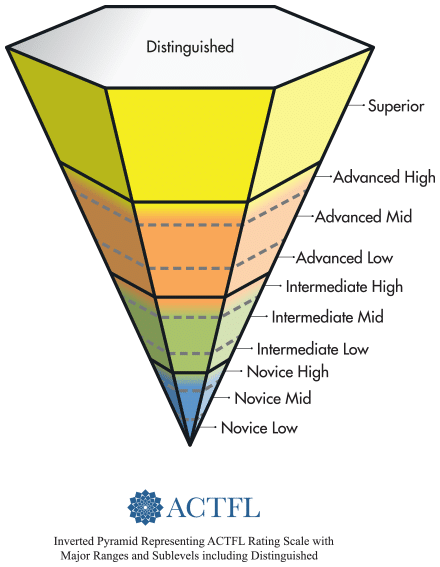
*Image source : Official ACTF website
ACTFL Proficiency Levels – Novice
Limited to communicating with short,simple memorised phrases. At the novice level, the individual will most likely have difficulty communicating with native speakers.
ACTFL Proficiency Levels – Intermediate
Can create sentences using learned words and phrases. At the intermediate level, the individual is able to ask and answer simple questions, and handle simple transactions.
ACTFL Proficiency Levels – Advanced
Can narrate and use past, present and future. At the advanced level, an individual can use paragraphs for complex situations and topics. Plus, they can handle unexpected complications with grammatical accuracy and fluency.
ACTFL Proficiency Levels – Superior
Can communicate with accuracy and fluency. At the superior level, an individual can discuss complex and abstract topics using supporting opinions and structured arguments.
ACTFL Proficiency Levels – Distinguished
Can communicate highly complex concepts. At the distinguished level, an individual is able to discuss global issues in a culturally appropriate manner. They can adapt their language to suit the situation and audience.
ACTFL Speaking
ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines can be used to evaluate speech that is either interpersonal (two-way) or presentational (one-way), and to determine a level among:
➤ Distinguished
Speakers at the Distinguished level can speak skillfully, and with accuracy, efficiency. They can produce highly sophisticated and tightly organised, extended speech.
➤ Superior
Superior-level speakers can participate clearly in autobiographical topics, as well as topics of community, national, or international interest. They can discuss their interests and areas of competence with ease, fluency, and accuracy.
➤ Advanced
Advanced-level speakers can speak skillfully, and with accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness. They can deal with unexpected complications in social situations. have sufficient control of basic structures and vocabulary to be understood by native speakers.
➤ Intermediate
Intermediate-level speakers are most easily understood by those accustomed to dealing with non-native learners of the language; They can speak about familiar topics related to their daily life.
➤ Novice
Novice-level speakers can communicate short, simple messages on highly predictable, everyday topics that affect them directly. They do so mostly through the use of isolated words and phrases.
ACTFL Listening
ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines can be used to evaluate how listeners understand spoken language, and to determine a level among:
➤ Distinguished
Distinguished-level listeners can understand a wide variety of forms, styles, and registers of speech on highly specialised topics, in language tailored to different audiences. They are able to understand unpredictable turns of thought related to sophisticated topics.
➤ Superior
These listeners can understand speech in a standard dialect on a wide range of familiar and less familiar topics. They can follow linguistically complex extended speech from a variety of sources.
➤ Advanced
These listeners can understand the main ideas and most supporting details in connected discourse on a variety of general interest topics. They have sufficient knowledge of language structure to understand basic time-frame references.
➤ Intermediate
Intermediate-level listeners understand speech that conveys basic information. This speech is simple, with familiar vocabulary. They can understand information conveyed in simple, sentence-length speech on familiar or everyday topics.
➤ Novice
These listeners can understand key words, and formulaic expressions that are highly predictable.tements, and commands. They typically require repetition, rephrasing, and a slowed rate of speech to understand what is being said.
ACTFL Reading
ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines are intended to describe what readers are able to understand from what they read, and to determine a level among:
➤ Distinguished
Distinguished-level readers can understand a wide variety of texts from many genres including professional, technical, academic, and literary. They are able to comprehend implicit and inferred information and tone. They are able to understand unpredictable turns of thought related to sophisticated topics.
➤ Superior
These readers can understand texts from many genres dealing with a wide range of subjects, both familiar and unfamiliar. Superior-level readers can understand texts that use specialised vocabulary and complex grammatical structures.
➤ Advanced
Advanced-level readers can understand the main idea and supporting details in narrative and descriptive texts. Advanced-level readers are able to understand texts that have a clear and predictable structure.
➤ Intermediate
These readers are able to understand simple, straightforward texts, such as messages found in highly familiar, everyday contexts. These listeners can understand information conveyed in simple, predictable, loosely connected texts.
➤ Novice
Novice-level readers can understand key words and simple phrases that are in a familiar context. These readers are best able to understand a text when they can anticipate the information in the text.
ACTFL Writing
These ACTFL Guidelines can be used to describe an individual’s use of written text that is either presentational (essays, reports, letters) or interpersonal (instant messaging, e-mail communication, texting). Then to determine a level among:
➤ Distinguished
Distinguished-level writers can carry out formal writing tasks such as official correspondence, position papers, and journal articles.
➤ Superior
These writers are able to produce most kinds of formal and informal correspondence, in-depth summaries, reports, and research papers on a variety of social, academic, and professional topics
➤ Advanced
Advanced-level writers can narrate and describe in past, present, and future, using paraphrasing and elaboration. They can write routine informal and some formal correspondence, and descriptions and summaries of a factual nature.
➤ Intermediate
These writers can write simple messages and letters, requests for information, and notes. Plus, they can ask and respond to simple questions in writing.
➤ Novice
Novice-level writers can create lists and notes, simple information on forms and documents. They can also transcribe or copy familiar words or phrases, or letters.

ACTFL Proficiency Tests List and Presentation
ACTFL proficiency tests are a set of reliable language proficiency tests, used worldwide. The tests are used by major corporations, academic institutions, and government agencies. They are widely regarded as the best language proficiency testing regime.
ACTFL administers over 700,000 tests per year in more than 120 languages in over 60 countries.
ACTFL proficiency tests assessing cover the 4 core language skills: speaking, writing, listening, reading.
ACTFL OPI – Oral Proficiency Test
The OPI is a 20-30 minute one-on-one interview with a certified ACTFL tester – a real person or computer avatar.
ACTFL WPT – Writing Proficiency Test
The WPT is a web-based test of the global assessment of functional writing ability in a language.
ACTFL LPT – Listening Proficiency Test
The LPT consists of 10 to 25 listening passages spoken in the target language. Listening passages vary in genre, content, length, and complexity, depending on the level being targeted.
ACTFL RPT – Reading Proficiency Test
The RPT consists of between 10 to 25 reading texts written in the target language.
IELTS/TOEFL Equivalency Table With the ACTFL Proficiency Scale
There are a number of testing scales in addition to ACTFL. The best known being TOEFL and IELTS, and each scale has its own method of scoring. It’s normal to be confused about understanding the difference between scores from different proficiency scales.
So it’s very useful to understand how a score in one scale compares to a score in another. The table below shows you comparative scores between ACTFL, TOEFL and IELTS.
| ACTFL | TOEFL | IELTS |
|---|---|---|
| Novice | 2.0 | |
| Intermediate | 3.0 | |
| Advanced low | 42 - 71 | 3.5 - 4.5 |
| Advanced mid | 72 - 94 | 5.0 - 6.0 |
| Advanced high | 95 - 120 | 6.5 - 7.5 |
| Superior | 8.0 - 9.0 |
Understanding your TOEFL iBT score:
We have compiled a list of articles that cover everything there is to know about the TOEFL score ! Feel free to check them out down below:
- How is the TOEFL scored?
- The TOEFL score range per section
- How to send your TOEFL score to US Universities?
- What happens if you fail the TOEFL?
Understanding your IELTS band score:
We have made a list of article covering everything there is to know about the IELTS score:
- How is the IELTS scored?
- How to check your IELTS results?
- Understanding the IELTS Indicator
- TOEFL Score to IELTS Conversion Chart
- IELTS to CLB conversion chart
- IELTS score requirements for a Canadian PR
- IELTS scores for Canadian Universities
- IELTS score for being a nurse in Canada
- How to send your IELTS score to US Universities
Improve Your English Skills Online With GlobalExam
GlobalExam is an online platform that helps candidates prepare for language proficiency tests. The content is developed by language tests experts, and updated everyday in order to be the closest to the tests. ACTFL Proficiency Test preparation is available on GlobalExam.
You’ll prepare the tests with a carefully designed online preparation method, with exercises and mock exams, including detailed correction. Results are automatically saved, so you can review your answers, analyse your progression and focus on your weaknesses.
You can try the free version of the platform before buying a Premium plan to unlock all the content! You just need to register to access the trial version.



